The team led by Professor He Zhongwei from the College of Economics and Management recently published a research paper titled "SHAP-ing Urban Sustainability: Integrating NDDF and LightGBM to Uncover Coordinated Pollution and Carbon Abatement Costs in Chinese cities" on the Sustainable Cities and Society (CAS Tier 1, IF=12.0). Ingeniously introducing the comprehensive analysis framework that integrates NDDF and LightGBM and also using the SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanation) method, the research systematically uncovers the coordinated pollution and carbon abatement costs in 287 Chinese cities during 2006-2019 as well as the affecting mechanism.

The research reveals a notable trend of phased changes in the costs of coordinated abatement of PM2.5 and CO₂ emissions in Chinese cities. In particular, economically developed regions, such as the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration, see much higher coordinated abatement costs than other regions.
The research also suggests employment and financial activities are the core factors affecting PM2.5 abatement costs, while industrial structures and industrial SO2 emissions are the key to CO2 abatement costs. In addition, energy consumption plays a bigger role in large cities, while population and economic variables are more important factors in small and medium cities.
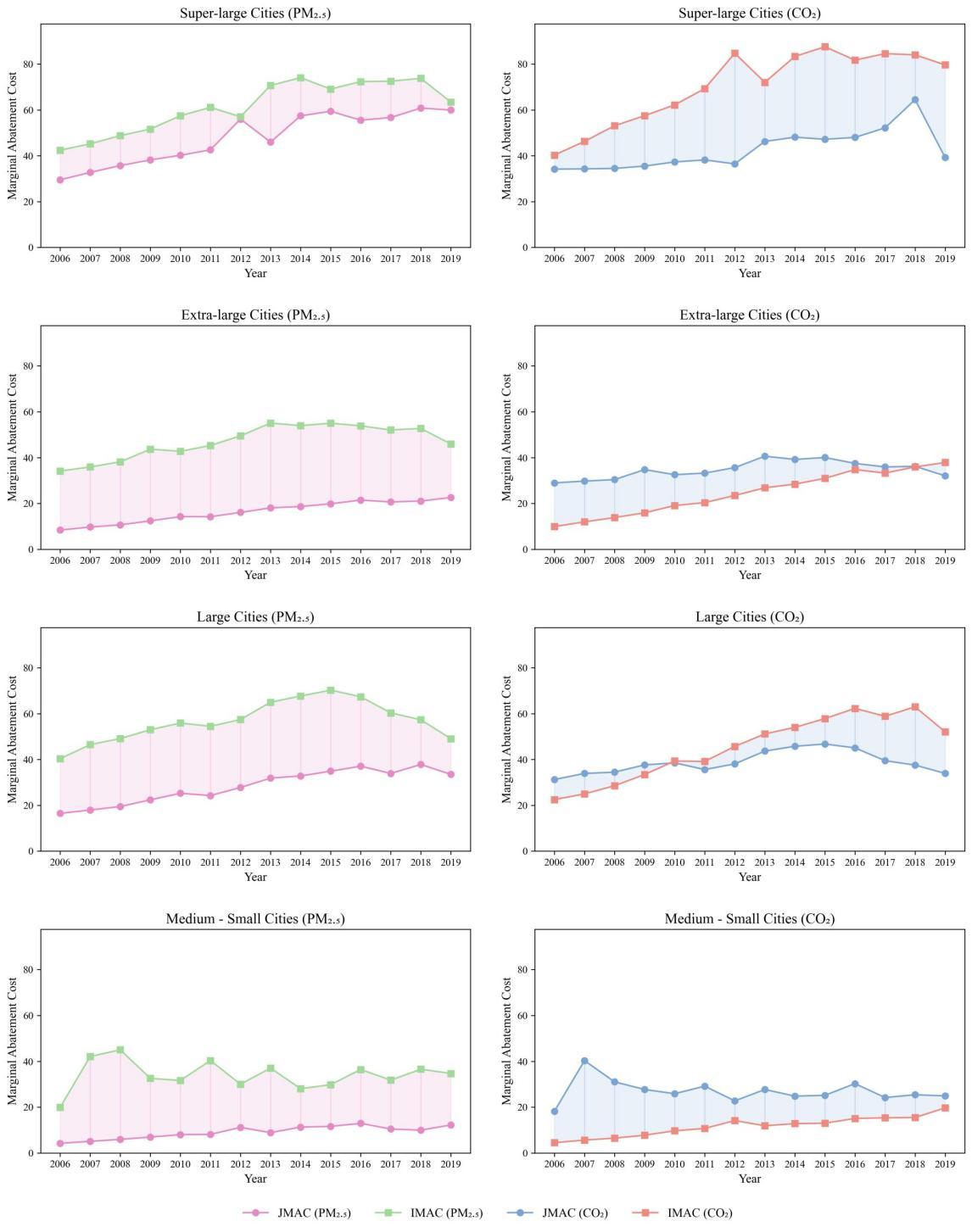
Based on the said findings, the research proposes that input in clean technology and green finance should be increased in economically developed regions, to advance industrial upgrade and optimization of the energy mix; in small and medium cities, green development capabilities should be enhanced with the focus on education, scientific research and treatment of agriculture pollution. Meanwhile, policy reforms intended to promote regional differentiation and scale sensitivity also serves as a critical path to reducing emission abatement costs and driving the sustainable development of cities.
Zhang Qiangqiang, a young teacher from the College of Economics and Management of BUA, is the first author of the paper, and Professor He Zhongwei is the corresponding author of the paper. The research is a Youth Science Foundation project under the National Natural Science Foundation (72303201), a key project of the Beijing Social Science Foundation (23JCB027), a 2024 special youth project under the 14th Five-year Plan of Beijing Municipality for the Development of Education Science (BCDA24141), a special humanities and social science project under the Social Sciences Prosperity Initiative of BUA (FRSK-2024-005), as well as a project funded by the Youth Innovation Team of Shandong schools of higher learning (2024KJL029). As global climate changes intensify and China further advances towards its "carbon peaking and carbon neutrality" goals, the research not only broadens the theoretical perspective for the coordinated pollution and carbon abatement in cities, but also provides an important practical reference for China and even other developing countries in formulating scientific and effective paths to low-carbon and green development.
The team members said, under the strong leadership of BUA's Party committee, they will center around the theme of "implementing the master plan for building China into an education powerhouse and advancing the high-quality development of BUA's educational endeavors", and work to honor the "year of practical action and pioneering excellence". Also, they will align research with national strategies and the capital's development needs, continuously deliver high-quality research outcomes, and make greater contribution to the high-quality development of BUA through real actions.
 LATEST NEWS
LATEST NEWS
 search
search


